Red Black Tree
In this post, I will introduce the red black tree, which is a kind of self-balancing binary search tree. Red black tree has more relaxed notion of balance than AVL trees, which is good enough to reduce the searching time and more easy to maintain the tree itself. Since red black tree is also a BST, so some tricky operation I introduction in this post also works in red black tree.
Self-Balanced Tree
Why we need balanced tree
Binary Search Tree is good, but BST may degenerate to a linked list while handling some kinds of input, in this case the time complex of BST operation would increase to \(O(N)\).
Let`s say, we insert array [1, 10, 2, 9, 3, 8, 4, 7, 5, 6] to BST, after insertion the BST would look like below:

So, to get the best performance we want to get a full tree, whatever our input are. In this case, any node`s left subtree should obtain the same number of node as the right subtree, which is a balanced tree.
2-3-4 Tree
A 2-3-4 Tree is a self-balancing tree, it allowed internal node obtain more than two child node. There are three type of internal node in 2-3-4 tree, which obtain 2/3/4 child node and the key in one node sorted from smallest to greatest, that`s where it`s name come from.
2-3-4 Tree has a special way to insert key, which makes it self-balance. Every time insert a new key to 2-3-4 tree, it first find a leaf node with the same process of BST, if the leaf node is full, which means it obtain 3 key already, split it to two node to store the smallest and greatest key, then insert the mid key to it`s parent, recurse the above process until find a not empty node store mid key or reach the root, the root node will split into three node and the mid key would be the new root. Finaly insert the key to the right leaf.
Here a demo for input above: 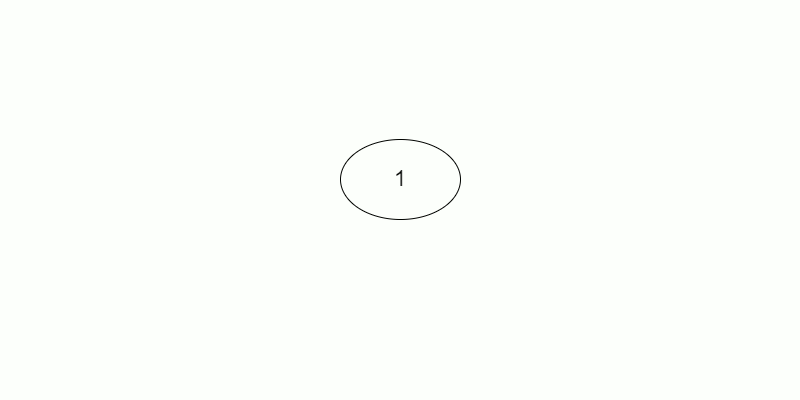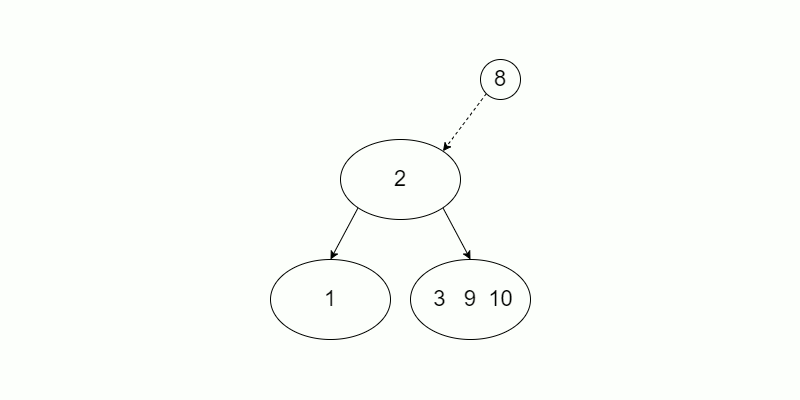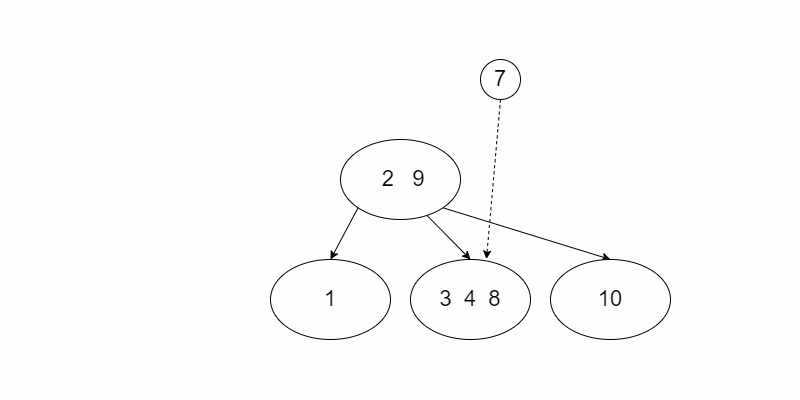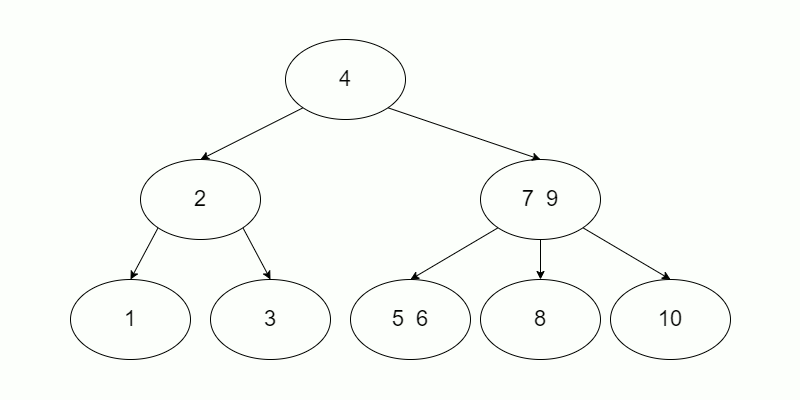
Notice that 2-3-4 tree kept balance in insert process. If we could do similar operation in BST, we would avoid the degenerate, and that`s what red black tree do.
Definition
A red-black tree is a binary search tree with the following additional properties:
1. Every node is either red or black.
2. Each NULL pointer is considered to be a black node.
3. If a node is red, then both of its children are black.
4. Every path from a node to a leaf contains the same number of black nodes. A red-black tree of \(n\) nodes, then the height \(h <= 2lg(n+1)\).
Operation
At this post we will talk about the bottom-up insert and delete. the complet implementation code in here
Rotation
a red-black tree balance itselft according to rotation. Basically, there are two type of rotate: left rotate(zig), right rotate(zag), each is inverse to the other. 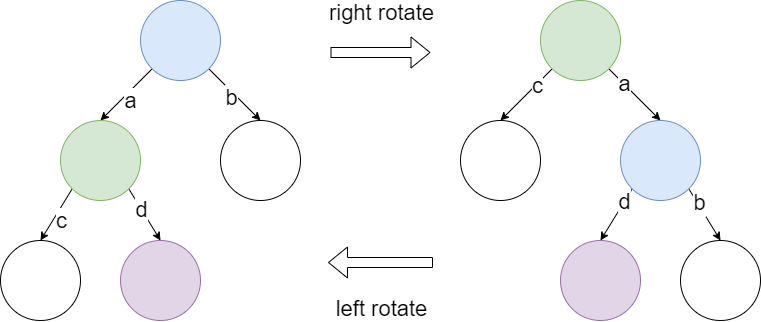
Insert
If we treat the edge between red node and it`s parent as glue, then we can correspond red-black tree node to 2-3-4 tree node just like below: 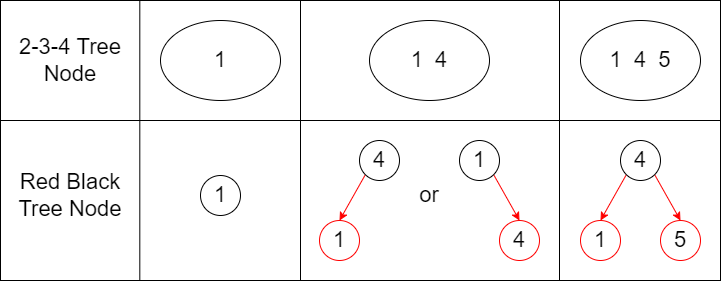 Remenber that a red node`s child must be black, which means there are no continued red node in red-black tree , so the 4 node is injective.
Remenber that a red node`s child must be black, which means there are no continued red node in red-black tree , so the 4 node is injective.
With this correspond table in mind, we could start insert.
First, we insert the key into red-black tree just like BST but paint that new insert node with color red, which could be seen as glue that node into the leaf node, just like 2-3-4 tree does.
Then we must check if the red node is legal if the node is not root:
- Case 1: if the parent is black we are just change a 2 node to a 3 node, no action needed and we are done.
- if the parent is red, we need check the color of the sib of parent, which we called it uncle node:
- Case 2: if the uncle is black, we are change a 3 node to a 4 node, which is legal in 2-3-4 tree, but violate the red-black tree rule 3, and we can fix it with rotation:
- if node is in the opposite position compare to parent related to grandparent, we must first rotate parent to fix it.
- if node and parent is in the same direction we rotate the grandparent to the opposite of parent fixed the continue red violate.
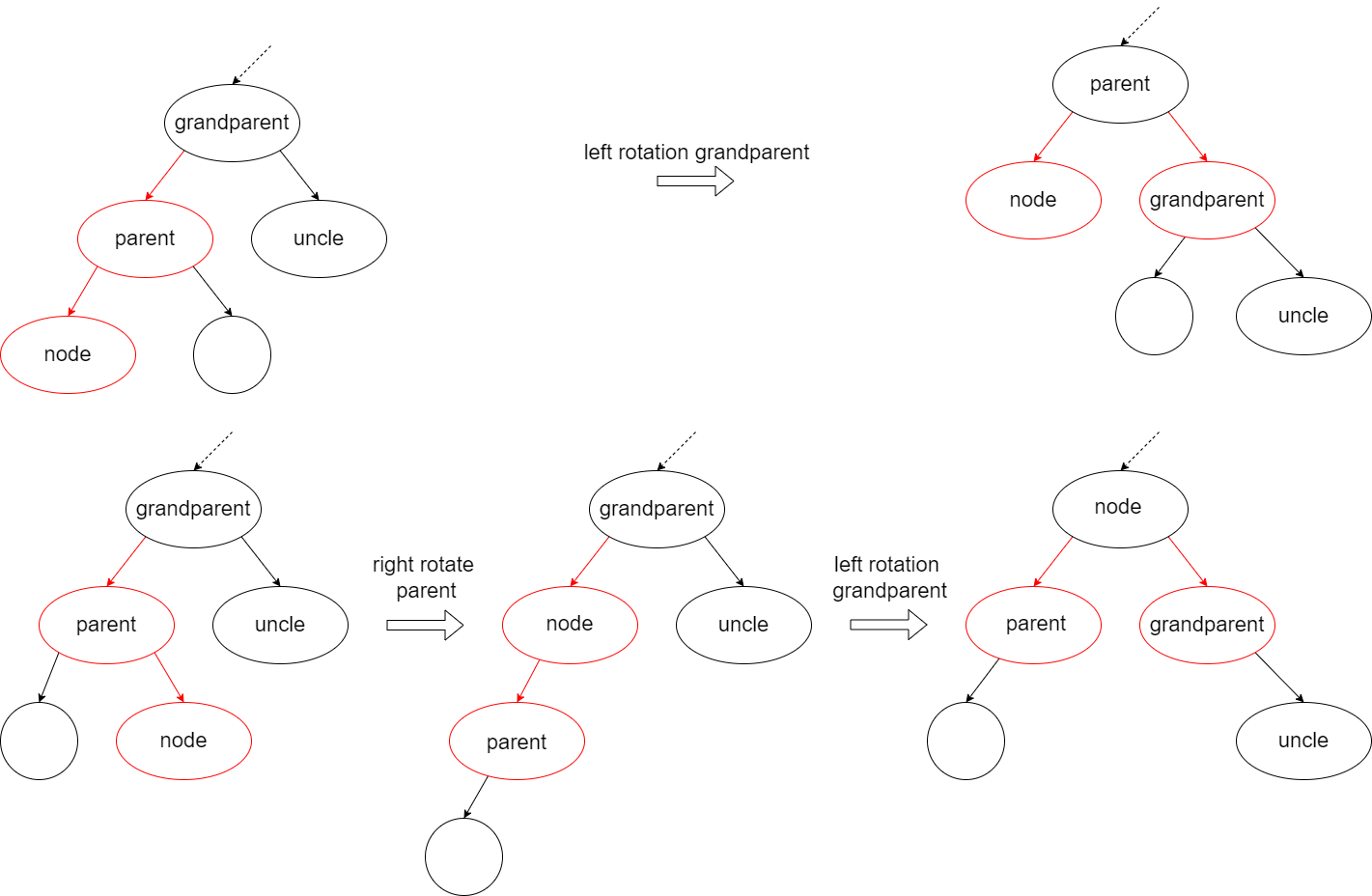
- Case 3: if the uncle is red, then the leaf node is already a 4 node, and should slipt, in red-black tree we just need to flip the color of parent, uncle and grandparent, since we are paint grandparent red, it must be checked as well.
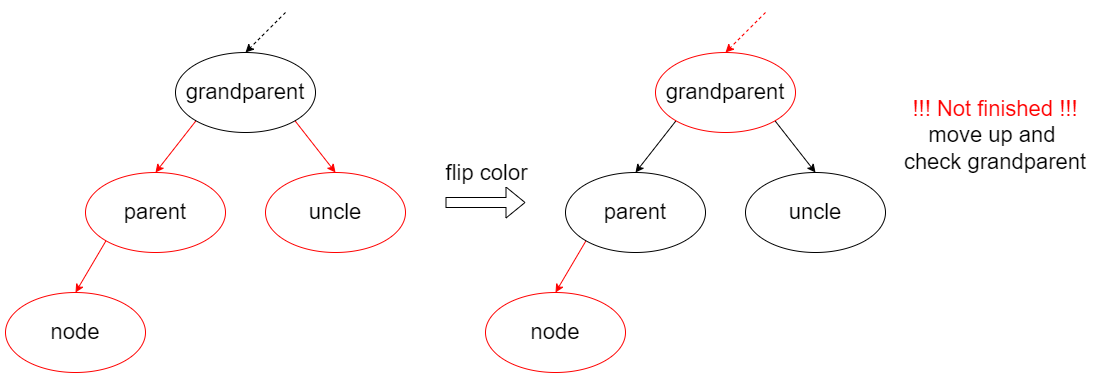
- Case 2: if the uncle is black, we are change a 3 node to a 4 node, which is legal in 2-3-4 tree, but violate the red-black tree rule 3, and we can fix it with rotation:
Finaly color root with black, and the insert is finished.
Notice that we only rotate in Case 2 and after rotate we are done, so there are at most two rotation every insert.
Though the picture above only shows the left case, the right case is just symmetric opration.
Here`s the demo for zig input: 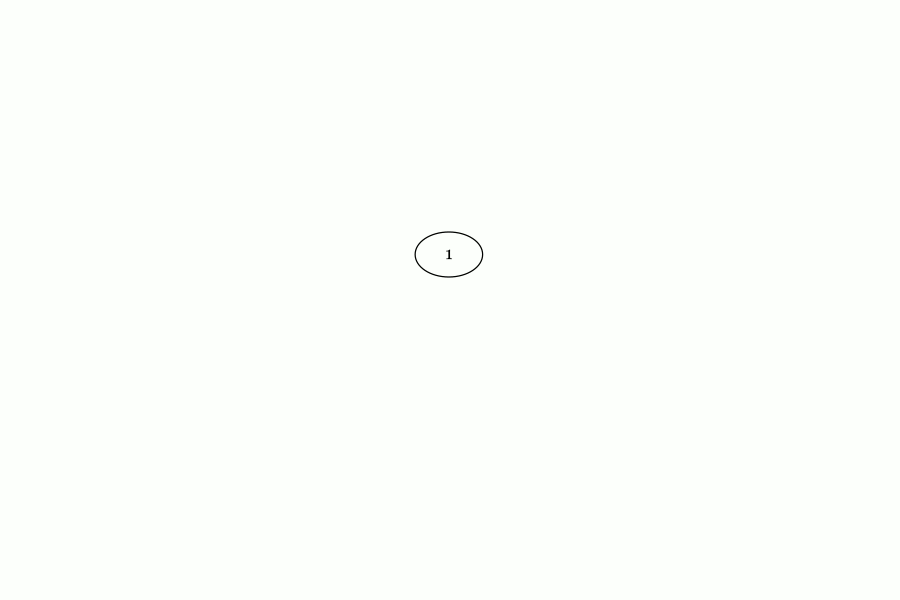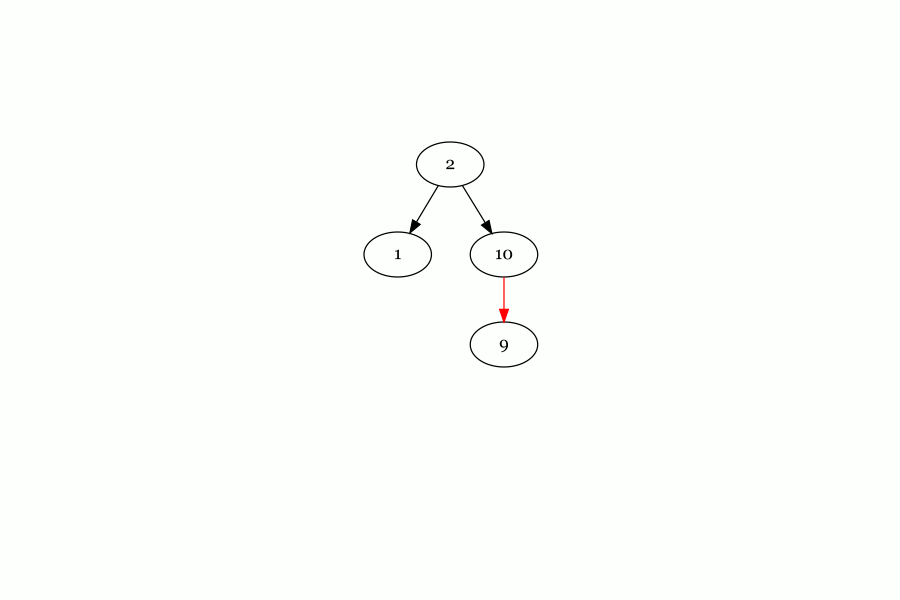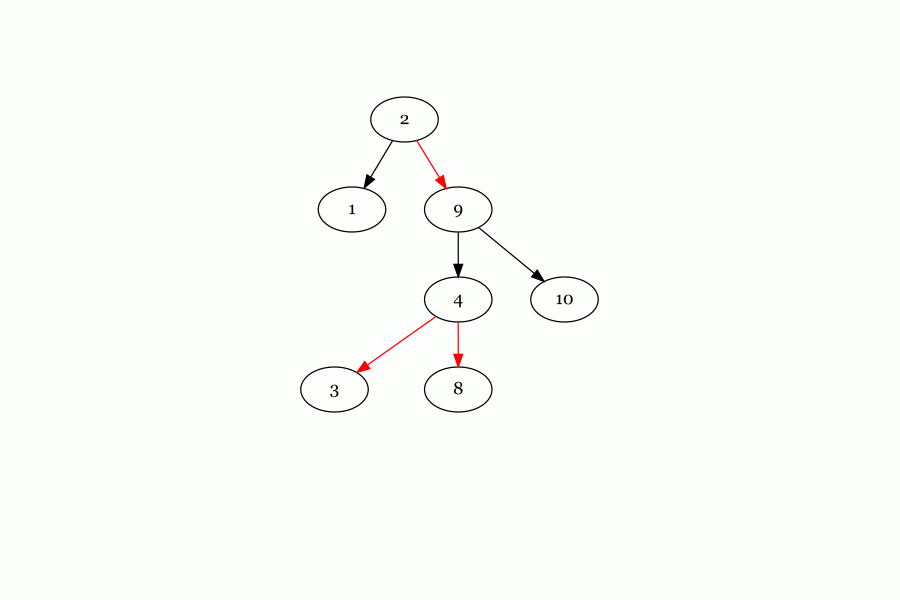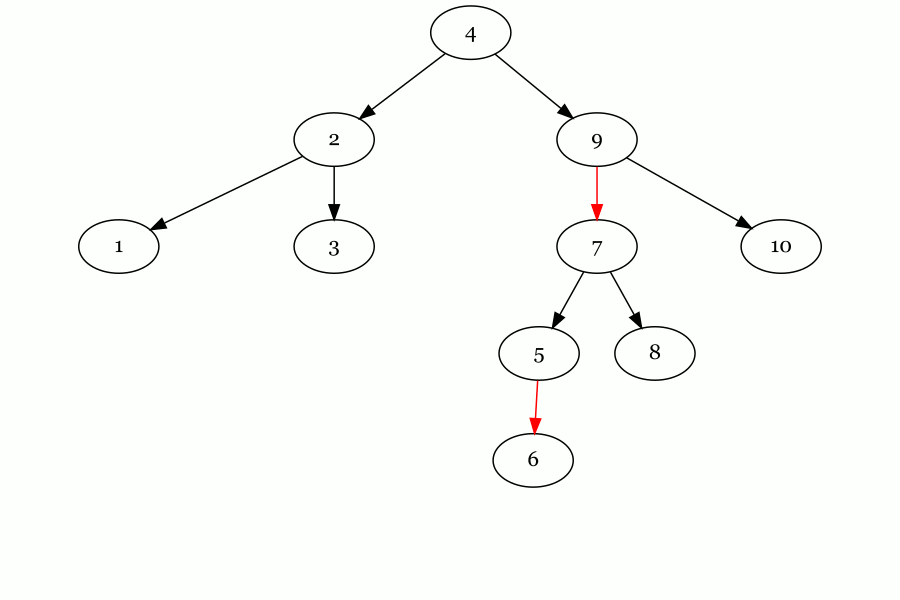
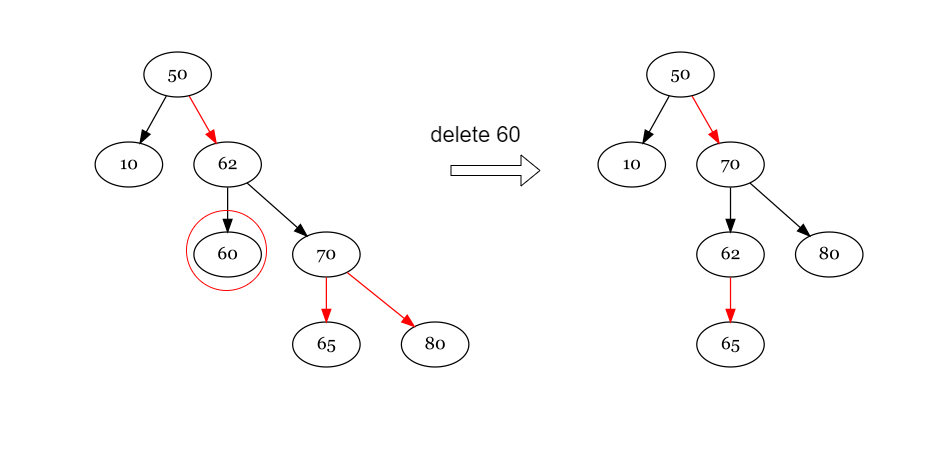
Delete
With the same idea of insert, we can assume that before delete our red-black tree is balanced, at least balanced as 2-3-4 tree does.
So we only need to keep balance in delete. The key idea is that we change some node from red to balck, that would increase one height. Here`s the step:
First find out the node should be delete by query key.
Then, check color of the node and it`s replace node and delete the target node, if either node is red, which means we are delete from a 3/4 node, color the replace node black and we are done. if both node is black, then the height of correspond 2-3-4 tree is broken and we need fix it with rotation:
- Preparation: If the sibling of replace node is red, we rotate parent to the replace node and update sibling information.
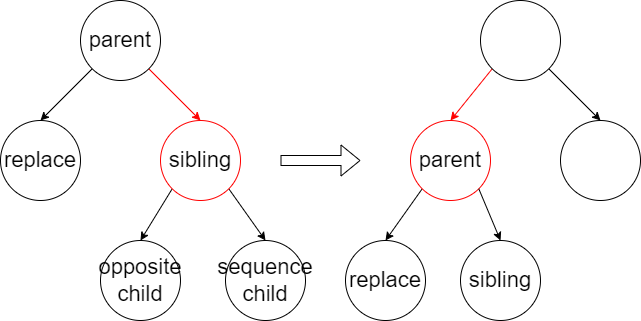
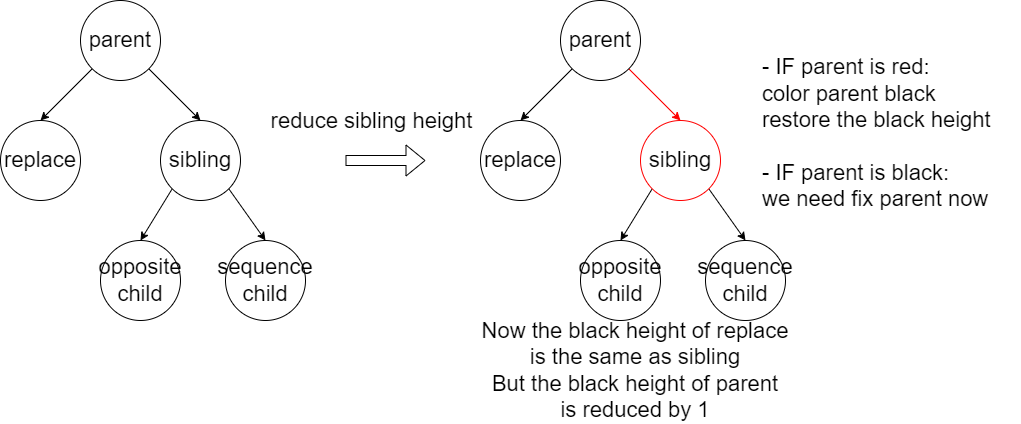
- Case 1: If both child of sibling is black, we color sibling red, and check parent color:
- If parent is red, color parent black and we are done.
- If parent is already balck, we must fix parent now.
- Case 2: At least one sibling child is red:
- If the red child is in opposite position, we rotate it to the sequence position first.
- the we rotate parent to the replace node direction and color the red chlid black and we are done.
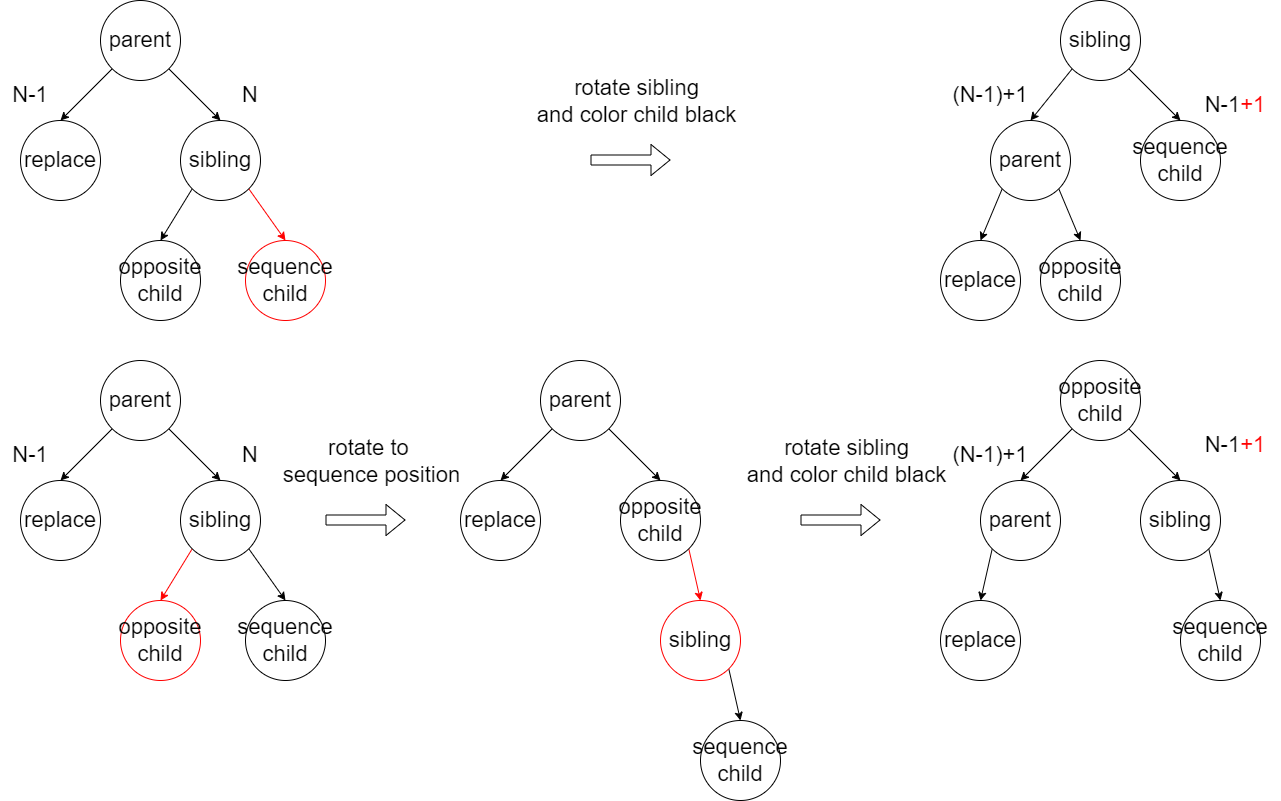
- If the red child is in opposite position, we rotate it to the sequence position first.
Notice that in case 2 we rotate at most twice and finish, though at the preparation we may rotate once, but that rotate guarantee we would end at parent, since it`s red now. So there are at most three rotation every delete. The picture only shows the left case, the right case is just summetric operation. Here`s the demo of delet: